100 Questions on Standardized ELA Assessment Tests
100 Questions on Standardized ELA Assessment Tests
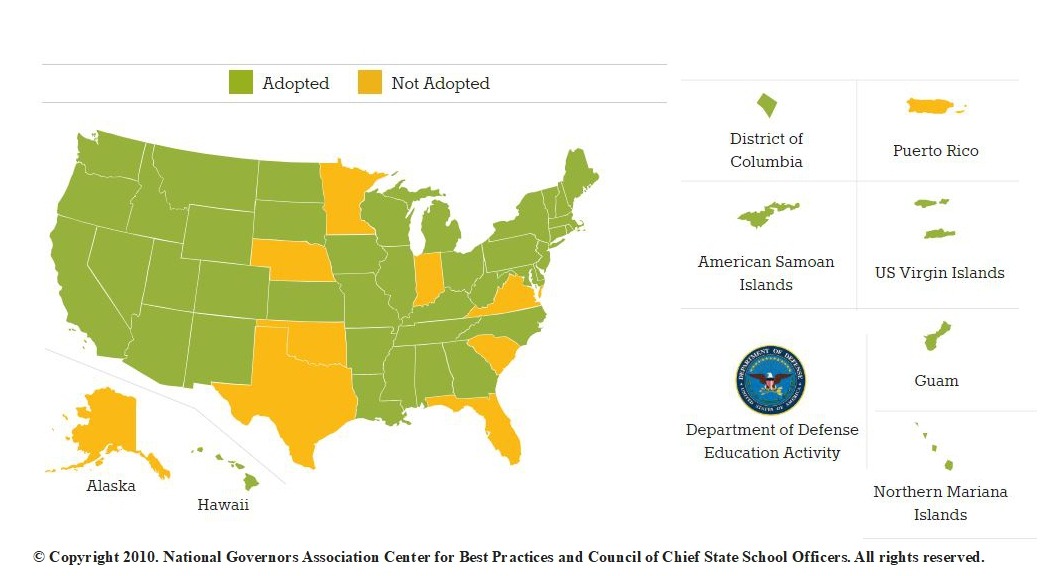
After having been an ELA teacher for 10 years, and then an assessment writer contracted with multiple Ed-Tech companies (while running my store Loving Language Arts) for about 10 years, I know all about what questions appear on English Language Arts standardized tests (not just in the spring, but all year long). You may be in one of the 41 states that adopted Common Core (College and Career Ready Standards) or not. Either way, these questions will surely appear on ELA assessment tests. I recommend having students practice answering them all year long. The questions are arranged by the target (demonstrable skill). They are based on K-12 anchor standards in reading, literacy in content areas, writing, language, and speaking & listening.
Table Of Contents
Citing Textual Evidence In Reading:
- Which [detail/sentence/line] from the text [indicates/best supports] [provide inference or conclusion based on the text]?
- Which [detail/sentence/line] from the text best supports this [inference/conclusion] OR best shows [provide inference or conclusion]?
- The reader can [infer/conclude] [provide inference or conclusion based on the text]. Which [detail/sentence/line] from the text best supports this [inference/conclusion] OR best shows [provide inference/conclusion]?
- The author/narrator [infers/concludes] that [provide inference/conclusion based on the text]. Which [detail/sentence/line] from the text best supports this [inference/conclusion] OR best shows [inference/conclusion]?
- Read this [inference/conclusion].
[provide inference or conclusion based on the text].
Which [detail/sentence/line] from the text best supports this [inference/conclusion]? - Which [details/sentences/lines] from the text [indicate/best support] [provide inference or conclusion based on the text]? Select [two /three] answers.
Elaborating on Ideas in Writing Using Evidence and Details:
- Writing Explanatory Brief Text: A student is writing a [insert type of text] about [insert purpose or topic of text]. Read the draft of the text and complete the task that follows. [Insert stimulus @ 200-250 words].The student does not have a [good/effective] or is missing a(n) [good/effective/clear] [introduction/conclusion]. Write an introduction that provides a clear [controlling idea/thesis]…OR Write a conclusion that [follows logically from the information OR is appropriate for the audience and purpose.
- Writing Explanatory Brief Text: A student is writing a[n] [insert type of text] about [insert purpose or topic of text]. Read the draft of the text and complete the task that follows [Insert stimulus @ 200-250 words, underlining sentences where elaboration is needed. Add student notes @ 70-80 words]. The student wants to develop more support for the [controlling idea/thesis/topic, etc.]…Use information/evidence/facts/examples, etc. from the student notes to [complete/develop/continue] the paragraph that begins with the underlined sentence.
- Writing Explanatory Brief Text: Choose [information/evidence/facts/examples, etc. depending on content of student notes] from the student notes and write a paragraph to develop the underlined [idea/topic, etc.]. [for stimuli structured as simple cause/effect, pro/con, compare/contrast, problem/solution] Using [relevant/appropriate] information from the student notes, write a paragraph to be added after the underlined sentence that develops [information on the effect of ; the cons of ; the solution to ; OR a comparison between (or contrast to) , etc.].
- Writing Explanatory Full Text: Create an explanatory writing assignment that flows naturally from the research scenario given in the Student Directions. An explanatory assignment must provide the following information:
A purpose for writing
Development of the topic with relevant facts, definitions, concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples
A clear direction driven by a thesis/controlling idea supported by evidence from the sources about the topic, body paragraphs that develop the topic, and a concluding statement or section that follows from the information - Writing Narrative Brief Text: A student is writing a [narrative/story] for the [insert where it will be read] about [insert purpose or topic of text].Read the draft of the [narrative/story] and complete the task that follows. [Insert stimulus @ 200-250 words, underlining sentence(s) where elaboration is needed]. The student wants to make the story more [exciting/interesting/descriptive, etc.]. Add dialogue [and/or description] to [replace/to come after] the underlined part of the story to show [what happens during that part of the story, what happens between two characters or events, etc. OR to develop the part about , etc.]. Add details [and/or dialogue] after the underlined part of the story [showing or describing , OR to develop the part about , etc.].
- Writing Narrative Brief Text: A student is writing a [narrative/story] for [insert where it will be read] about [insert purpose or topic of text]. Read the draft of the [narrative/story] and complete the task that follows. [Insert stimulus @ 200-250 words] STEMS: The student’s [narrative/story] does not have a [good/effective] [or is missing a] [beginning/ending]. Write a beginning* for the [narrative/story] that [sets up the action to come, and/or shows what is going on at the beginning of the narrative, and/or explains/introduces who the characters is/are, or what the setting or mood is]. Write an ending* for the story that solves [or finishes the story by solving] the problem in the story. Write an ending* to the narrative that [follows logically from and/or reflects on, OR provides closure for and/or reflection on] the [events/experiences] in the narrative.
- Writing Narrative Full Text: Create a narrative writing assignment that flows naturally from the research scenario given in the Student Directions. A narrative assignment must provide the following information:
A purpose for writing
A conflict or “jumping-off” point
In-depth description, narrative techniques (such as dialogue), and a resolution - Writing Argumentative Brief Text: A student is writing a[n] [argumentative topic] for the [newspaper/mayor/school board/town/city council/principal, etc.] about…Read the draft of the and complete the task that follows. [Insert stimulus @ 200-250 words – no student notes for organization] …The text does not have [or is missing] an [appropriate/effective] [introduction/conclusion]…Write an introduction to the [argumentative topic] that [establishes, introduces, and/or sets up the context for] a clear claim about…Write a conclusion that [follows logically from the argument/is appropriate for the audience of] the [argumentative topic]…
- Writing Argumentative Brief Text: A student is writing a[n] [argumentative topic] about…for the [newspaper/mayor/school board, town/city council/principal, etc.]. Read the draft of the and complete the task that follows. [Insert stimulus @ 200-250 words, underlining sentences where elaboration is needed. Add student notes @ 70-80 words] The student wants to develop more [support for the claim/evidence to address the counterclaim] in the [argumentative] . Use [information/evidence/facts/details, etc. depending on content] from the student notes to develop a supporting paragraph that begins with the underlined sentence. Choose relevant evidence [and examples/facts, etc. depending on the content of the student notes] from the student notes and write one or two paragraphs to [further develop the underlined (claim/reason, etc.) OR address the underlined counterclaim]. Using information in the student notes, [write a paragraph to be added after the underlined sentence OR continue the paragraph that starts with the underlined sentence] that states [and argues against/addresses] the [counterclaim, or opposing point of view].
- Writing Argumentative Full Text: Create an argumentative writing assignment that flows naturally from the research scenario given in the Student Directions. An argumentative assignment must provide the following information:
A purpose for writing
A description of the audience
A topic with multiple sides, one of which the student can argue supported by evidence from the sources about the topic.
Determining Central Ideas and Supporting Details in Reading:
- Which [sentence/statement] best [identifies/expresses/shows] the [theme/central idea] of the text?
- Which [sentence/statement] best [identifies/expresses/shows] the [theme/central idea] of the [story/poem] told by the [narrator/speaker]?
- Which [sentence/statement] best [identifies/expresses/shows] [the author’s/character’s name’s] message about [provide theme/central idea]?
- Read the [sentences/lines/paragraph(s)]. [excerpt from text]
- What is the [theme/central idea] of the [sentences/lines/paragraph(s)]?
- Which [sentences/lines/paragraph(s)] from the text best [identify(ies)/express(es)/show(s)] the [theme/central idea]?
- Which sentence best summarizes the [first paragraph/introductory paragraph]?
- Read the [sentences/lines/paragraph(s)]. [excerpt from text] Which sentence best summarizes the [sentences/lines/paragraph(s)]?
- Which sentence best summarizes the text?
- Which sentence best summarizes what happens after [provide plot]?
- Read this summary.
[summary of a section of the text; one key detail/event is missing] Which [key detail/event] is missing from the summary?
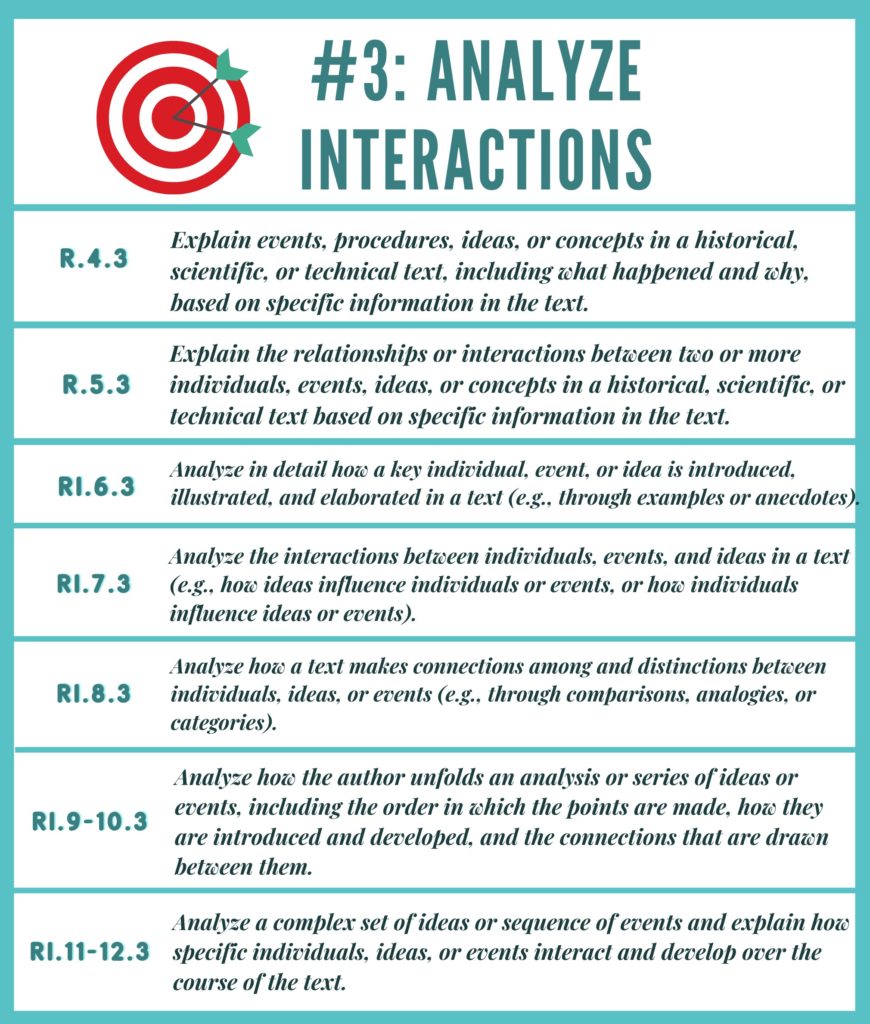
Analyzing How Ideas are Developed and Elaborated in Reading:
- How does the author’s inclusion of paragraphs [insert paragraph numbers] contribute to the text? NOTE: Item must focus on the
interaction between elements - How do [events/people/ideas/topics] develop over the course of the text?
- What does the use of [development/description of events/people/topics] show about [description of idea/content of text]?
- Which statement best describes how the use of [events/people/ideas/topics] affects both texts?
- How does the author’s inclusion of [provide individuals/events/ideas/etc.] add to the development of the text?
- How do(es) the [provide individuals/events/ideas/etc.] change the text?
- Read the [sentence(s)/paragraph(s)/section(s)].
[Provide excerpt from text] How does the [sentence(s)/paragraph(s)/section(s)] add to the development of the text? - How does the author’s inclusion of [provide individuals/ideas/events/etc.] add to the development of the text? Select [two/three] options.
Determine Word and Phrase Meanings (Including Domain-Specific, Figurative Language, and Nuances in Language):
- Read the sentence(s).
[Provide directly excerpted sentence(s) from text, with targeted word/phrase underlined] What is the meaning of the [word/phrase] [targeted word/“targeted phrase”]? - Read the sentence(s). [Provide directly excerpted sentence(s) from text, with targeted word/phrase underlined]. What does the [word/phrase] [targeted word/“targeted phrase”] most likely [suggest/mean]?
- Read the sentence(s). [Provide directly excerpted sentence(s)from text, with targeted word/phrase underlined]. Which [word(s)/phrase] best state(s) the meaning of [targeted word/“targeted phrase”]?
- Read the sentence(s). [Provide directly excerpted sentence(s) from text, with targeted word/phrase underlined] What does the use of the [word/phrase] suggest?
- Read the sentence(s). [Provide directly excerpted sentence(s) from text, with targeted word/phrase underlined]. The [word/phrase] [targeted word/phrase] has multiple meanings. What does the [word/phrase] [targeted word/“targeted phrase”] most likely suggest about [idea/event/topic/etc.] in the text?
- Read the sentence(s). [Provide directly excerpted sentence(s) from text, with targeted word underlined] A(n) [antonym/synonym] is a word that means the [opposite/same or nearly the same] of another word. What is the [antonym/synonym] of [targeted word]?
- Read the sentence(s). [Provide directly excerpted sentence(s) from text, with targeted word underlined] An analogy is a comparison between two things. What is the analogy of the [provide targeted word]?
- Read the sentence(s). [Provide directly excerpted sentence(s) from text, with targeted word/phrase underlined]. Select the [word/phrase] that best defines [targeted word/“targeted phrase”] as it is used in the sentence(s).
- Read the sentence(s) [Provide directly excerpted sentence(s) from text, with targeted word/phrase underlined]. What does the author communicate to the reader with the use of [targeted word/“targeted phrase”]?
- Read the dictionary entry.
(part of speech) 1. [definition]
Which [word/phrase] in the text best matches the dictionary entry? - Read the sentence(s). [Provide directly excerpted sentence(s) from text, with targeted word underlined]. What does the [root/affix] in the word [targeted word] mean?
- [Provide directly quoted sentence(s)/paragraph(s) from text, with targeted word or phrase underlined] What effect does the author create by using the [word/phrase] [targeted word/“targeted phrase”]?
- Read the [sentence(s)/paragraph(s)]. [Provide directly quoted sentence(s)/paragraph(s) from text, with targeted word or phrase underlined]. Which statement best describes what the [provide figurative language] in the [sentence(s)/paragraph(s)] adds to meaning of the text?
- Read the [sentence(s)/paragraph(s)]. [Provide directly quoted sentence(s)/paragraph(s) from text, with targeted word or phrase underlined] How does the [word/phrase] [targeted word/“targeted phrase”] affect the reader’s interpretation of the meaning of the text?
- How does the author’s use of the word/phrase [targeted word/“targeted phrase”] help the reader understand [the author’s/quoted person’s] [feelings/opinion/belief(s)] about [provide idea]?
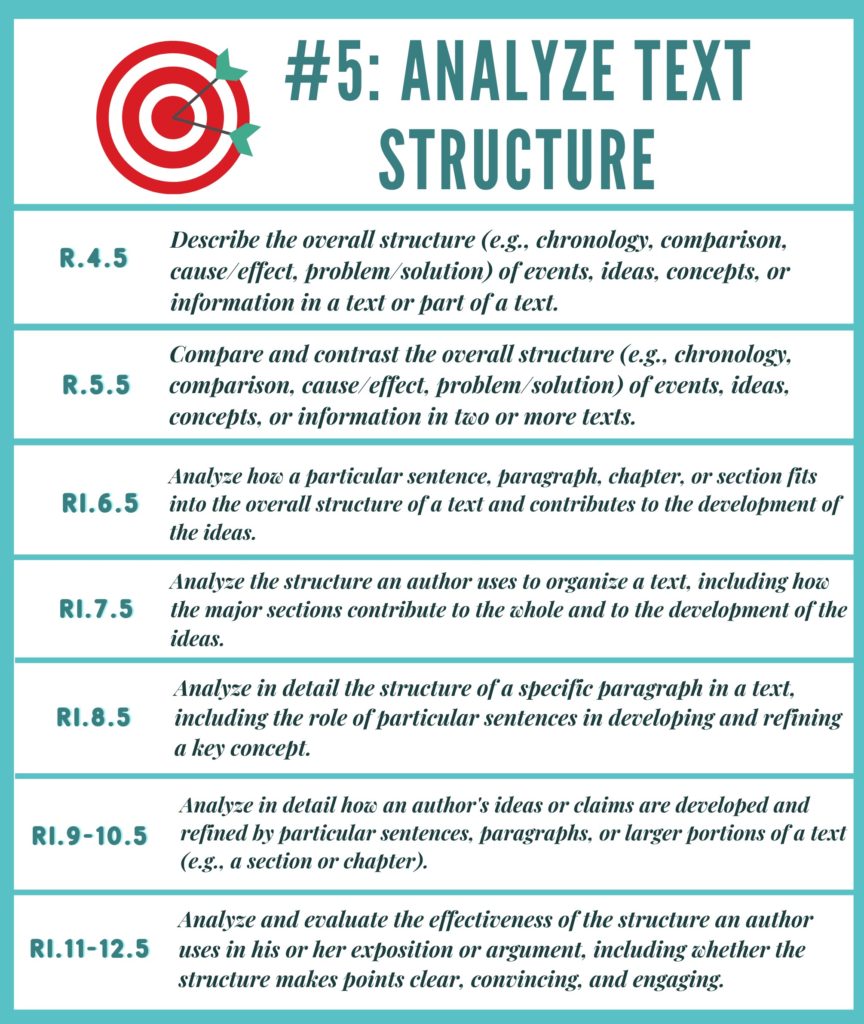
Analyzing Text Structure:
- What effect does [provide text structure/format/feature/etc.] have on the meaning of the text OR reader’s understanding of [provide element affected by structure, such as the structure of the central idea, presentation of information, or the structure of events in the text]?
- What is the most likely reason the author [used/included] [provide text structure/format/feature/etc.] in the text?
- The author [used/included] [provide text structure/format/feature]. What is the most likely reason the author structured the text this way?
- The author [used/included] [provide text structure/format/feature/etc.]. How does this structure affect [provide element affected by structure, such as central idea, presentation of information, or events]?
- How does the [first paragraph/first section/introduction] about [provide content in text] [add to/affect] [provide element affected by structure, such as central idea, presentation of information, or events]?
- How do(es) the [sentence(s)/paragraph(s)/section(s)] about [provide content in text] [add to/affect] [provide element affected by structure, such as central idea, presentation of information, or events]?
- [Provide direct excerpt] Which of these best describes why the author [began with/ended with/used] [this/these] [sentence(s)/paragraph(s)/heading(s)/question(s)/quotation(s)/etc.] in the text?
- [Provide direct excerpt] Why is the difference between [this/these] [sentence(s)/paragraph(s)/section(s)] and the one(s) that came [before it/after it] important to the text?
- [Provide direct excerpt] Select the statement that best explains why the author chose to include [this/these] [sentence(s)/paragraph(s)/section(s)].
- Why did the author choose to [begin/end] the text with [provide structure (paragraph/section/event/feature/etc.)?
- Why is using [provide text structure] important to understanding [the author’s point of view/author’s purpose/specific information/events/etc.] in the text?
- What does the author accomplish by [using/beginning with/ending with/including] [provide structure] in the text?
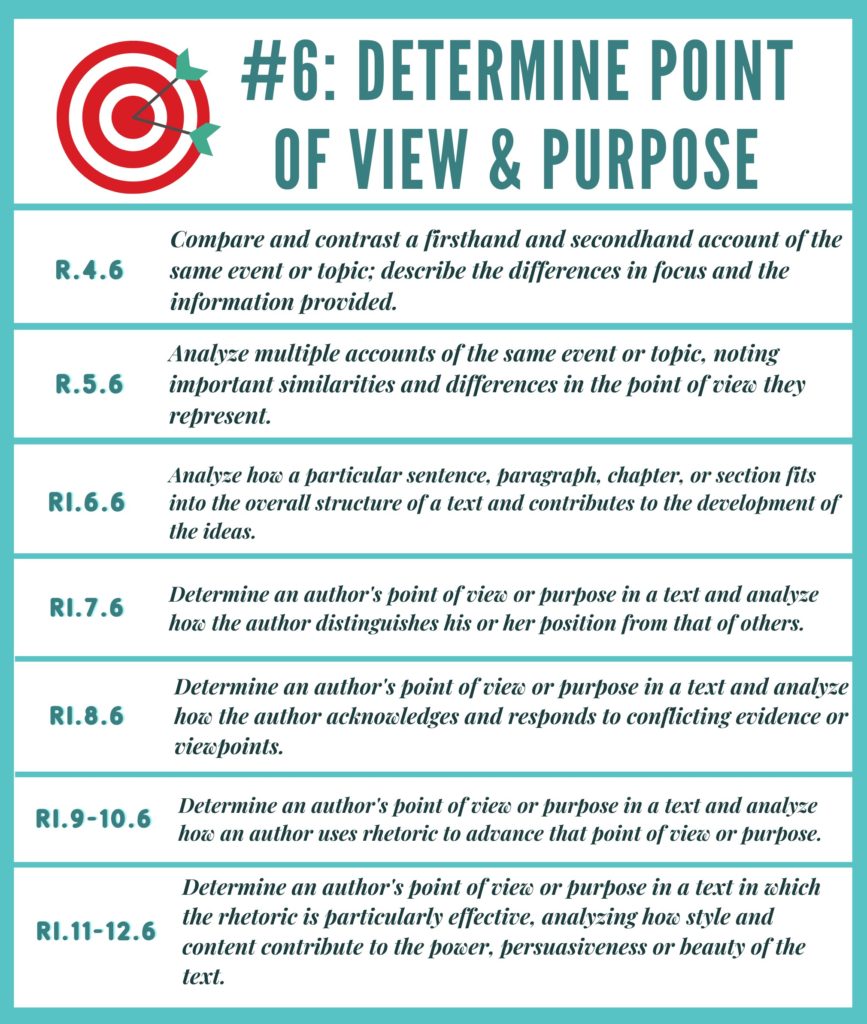
Determining Author’s Point of View or Purpose:
- What does the information in the [first paragraph/first section/introduction] of the text reveal about the author’s [point of view/purpose]?
- How does the author’s inclusion of paragraphs [insert paragraph numbers] contribute to the text? NOTE: Item must focus on the
author’s point of view or purpose - Read the [sentence(s)/paragraph(s)/section(s)]. [Provide excerpt from text] What does the information presented in the text reveal about the author’s [point of view/purpose]?
- PART A: Which of these inferences (or conclusions) about the [provide author’s point of view/author’s purpose] is supported by the text? PART B: Which [sentence(s)/paragraph(s)/section(s)] from the text best support(s) your answer in PART A?
- PART A: What inference (or conclusion) can be made/drawn about the
PART B: Which [sentence(s)/paragraph(s)/section(s)] from the text best [show(s)/tell(s)/describe(s)] the [inference made/conclusion drawn] in PART A? - PART A: What inference (or conclusion) can be made/drawn about the author’s opinion of [provide key individual/event/idea in the text]?
- What is most likely the author’s intent by mentioning [provide focused detail] in the text?
- Read the [sentence(s)/paragraph(s)/section(s)]. [Provide excerpt from text] What does the information presented in the text tell the reader about the author’s [point of view/purpose]?
Evaluating Visuals and Media:
- What effect does [provide feature/etc.] have on the meaning of the text OR reader’s understanding of [provide element affected by feature]?
- How does [provide feature/etc.] affect [or add to] the reader’s understanding of the text?
- What information does the reader learn in the [media or visual] that was not expressed in the text?
- How does the author use [media or visual element] to develop ideas [or a concept] in the text?
- What is the most likely reason the author [used/included] [provide text feature/etc.] in the text?
- The author [used/included] [provide feature]. What is the most likely reason the author [used/included] [provide feature]?
- The author [used/included] [provide feature/etc.]. How does this [provide feature/etc.]. affect [provide element affected, such as central idea, presentation of information, or events]?
- Why is using [provide text feature] important to understanding [the author’s point of view/author’s purpose/specific information/events/etc.] in the text?
- What does the author accomplish by [using/beginning with/ending with/including] [provide feature] in the text?
- PART A: Which of these inferences (or conclusions) about [provide how media is used] is supported by the text? PART B: Which [sentence(s)/paragraph(s)/section(s)] from the text best support(s) your answer in PART A?
- PART A: What inference (or conclusion) can be made/drawn about [provide how media is used]? PART B: Which [sentence(s)/paragraph(s)/section(s)] from the text best [show(s)/tell(s)/describe(s)] the [inference made/conclusion drawn] in PART A?
Evaluating Arguments, Claims, and Reasoning:
- What inference (or conclusion) can be made/drawn about the [provide relevance of evidence/elaboration to support claims, concepts, and ideas/etc.]? Explain using key evidence from the text to support your answer.
- What inference (or conclusion) can be made/drawn about the [provide relevance of evidence/elaboration to support claims, concepts, and ideas/etc.]? Explain using key evidence from the text to support your answer.
- Based on the text, [what conclusion can be drawn/what can a reader conclude] about [the author/the speaker/the narrator/or provide individual’s name]’s [thoughts/beliefs] about [provide individual’s name/provide information about individual/idea/event in the text]? Explain using key evidence from the text to support your answer.
- PART A: Which of these inferences (or conclusions) about how [provide relevance of evidence/elaboration to support claims, concepts, and ideas/etc.] is supported by the text?
- PART A: What inference (or conclusion) can be made/drawn about how [provide relevance of evidence/elaboration to support claims, concepts, and ideas/etc.]?
- PART B: Which [sentence(s)/paragraph(s)/section(s)] from the text best support(s) your answer in Part A? OR Which [sentence(s)/paragraph(s)/section(s)] from the text best [show(s)/tell(s)/describe(s)] the [inference made/conclusion drawn] in Part A?
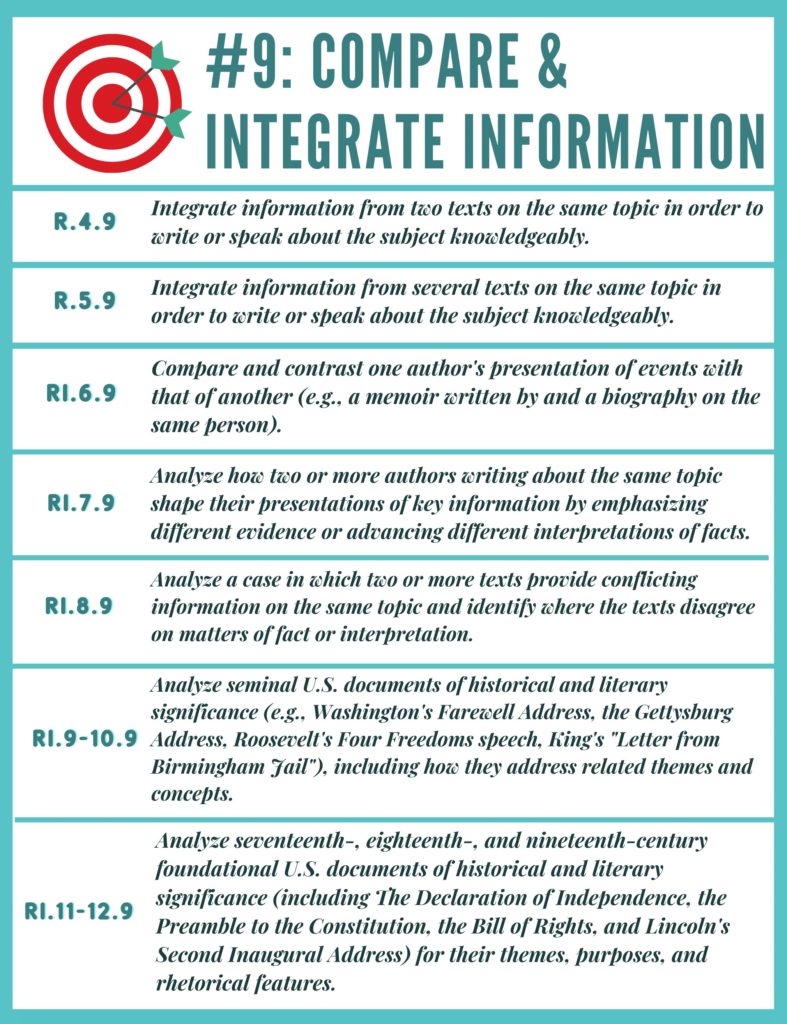
Comparing Two or More Texts & Perspectives:
- How does author #1’s viewpoint about…compare or contrast to author #2’s viewpoint on the same topic?
- Read the [sentence(s)/line(s)/set of lines/paragraph(s)] from [title text #2]. [excerpt from text] Based on this information, [what inference can be made/what can a reader infer OR what conclusion can be drawn/what can a reader conclude] about [the author/the speaker/the narrator/or provide individual’s name]’s [thoughts/beliefs] about [provide individual’s name/provide information about individual/idea/event] in [title text #1]? Explain using key evidence from [title text #1/both texts] to support your answer.
- PART A: Which of these inferences (or conclusions) about how the [provide key individual/event/or idea is introduced/illustrated/elaborated; OR author’s point of view/author’s purpose/relevance of evidence/elaboration to support claims, concepts, and ideas/etc OR conflicting viewpoints.] is supported by the text?
- PART A: What inference (or conclusion) can be made/drawn about the author’s opinion of [provide key individual/event/idea in the text]?
- PART A: What is most likely the author’s intent by mentioning [provide focused detail] in the text?
- PART A: Read the [sentence(s)/paragraph(s)/section(s)] from [title text #2]. [Provide excerpt from text]. Based on this information, [what inference can be made/what can a reader infer OR what conclusion can be drawn/what can a reader conclude] about how the [provide key individual/event/or idea is introduced/illustrated/ elaborated OR author’s point of view/author’s purpose/relevance of evidence/elaboration to support claims, concepts, and ideas/etc OR conflicting viewpoints.] in [title text #1]?
- PART B: Which [sentence(s)/paragraph(s)/section(s)] from the text best support(s) your answer in Part A?
Reading Literary Nonfiction and Complex Texts in Content Areas:
- The author uses a common literary theme to report on an event which is the theme of [theme such as “man versus nature”]. Select two details the author uses to develop this theme in the text.
- The author uses parallel structure in this excerpt. What is the author’s purpose for using this structure?
- The author uses loaded language to describe…What are some examples of loaded language the author uses?
- The author uses figurative language to describe…How does the author describe the same thing through facts elsewhere in the text?
- Which of the following details from the text are hyperbole (exaggerations) that are not meant to be taken literally?
- What effect does the author create with the use of [literary device]?
You Know What Else Kids Love?
Click below for FREE ELA PRACTICE TESTS – each targeting specific reading, writing, language, and speaking/listening/viewing standards.
Check out these GRADE-SPECIFIC test prep books with practice tests that target EVERY GRADE-SPECIFIC READING INFORMATIONAL TEXT STANDARD, one by one. An added bonus is that students LOVE the texts! In Easy-Print or Self-Grading Online Versions.
How about save this pin to your “ELA Test Prep” Board so that you can come back to this post again?